At the posterior aspect of the knee? lies the popliteal fossa. It is a diamond shaped♦️area that holds several important nerves and vessels that travel from the thigh to the knee. In this snippet we will take a closer look at its borders and contents.
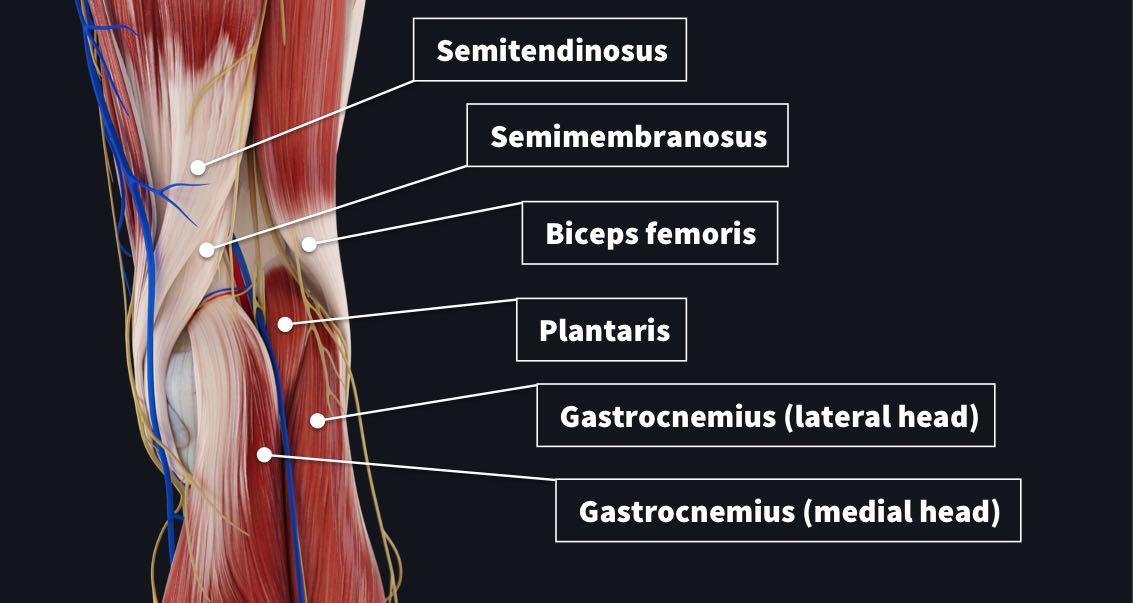
The popliteal fossa has 4 main borders made from posterior muscles and tendons of the leg and thigh;
- Superomedial border = Tendons of semimembranosus with the semitendinosus superficial to it
- Superolateral border = Tendon of biceps femoris
- Inferomedial border = medial head of gastrocnemius
- Inferolateral border = lateral head of gastrocnemius and plantaris
The floor of this fossa is comprised of the posterior surface of the knee joint capsule, popliteus muscle and posterior femur. The roof contains popliteal fascia and skin.
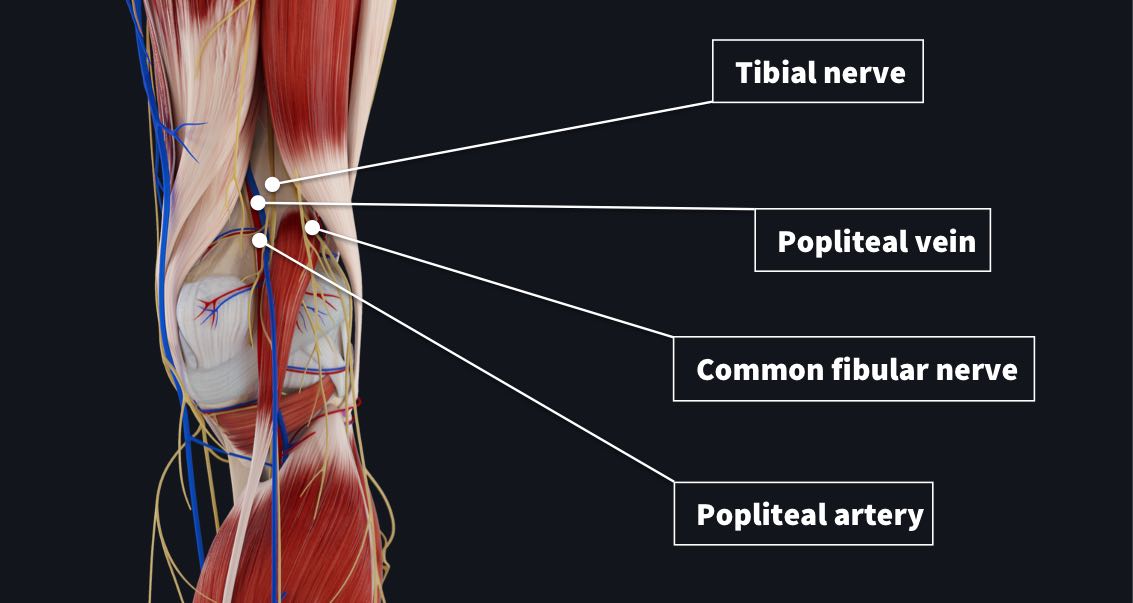
Within the popliteal fossa 4 main neurovascular structures are seen traveling from the thigh to leg;
- Popliteal artery– deepest structure, continuation of femoral artery
- Popliteal vein- the small saphenous vein passes between the two heads of gastrocnemius to empty into popliteal vein
- Tibial nerve– most superficial, branch of sciatic nerve
- Common fibular nerve– most superficial, branch of sciatic nerve and travels along lateral margin of fossa
You can use the mnemonic SAVNB (Serve And Volley Next Ball) to remember the popliteal fossa anatomy medial-to-lateral in arrangement. Semimembranosus, Artery, Vein, Nerve, Biceps femoris.
Damage to this area from trauma can result in swelling known as a popliteal aneurysm. Meaning an artery has been dilated greater than 50% of its normal size. This is particularly dangerous in this area due to popliteal fascia being non-extensible. Thus, an aneurysm could affect the inner contents of the fossa. For instance, the tibial nerve could be compressed resulting in weakened/absent plantar flexion, or paraesthesia of the foot and posterolateral leg. Luckily such conditions can be diagnosed by a professional health care provider by palpating the area ?⚕️?⚕️⚕️.
If you found this blog post useful, you might also enjoy learning about the unhappy triad.