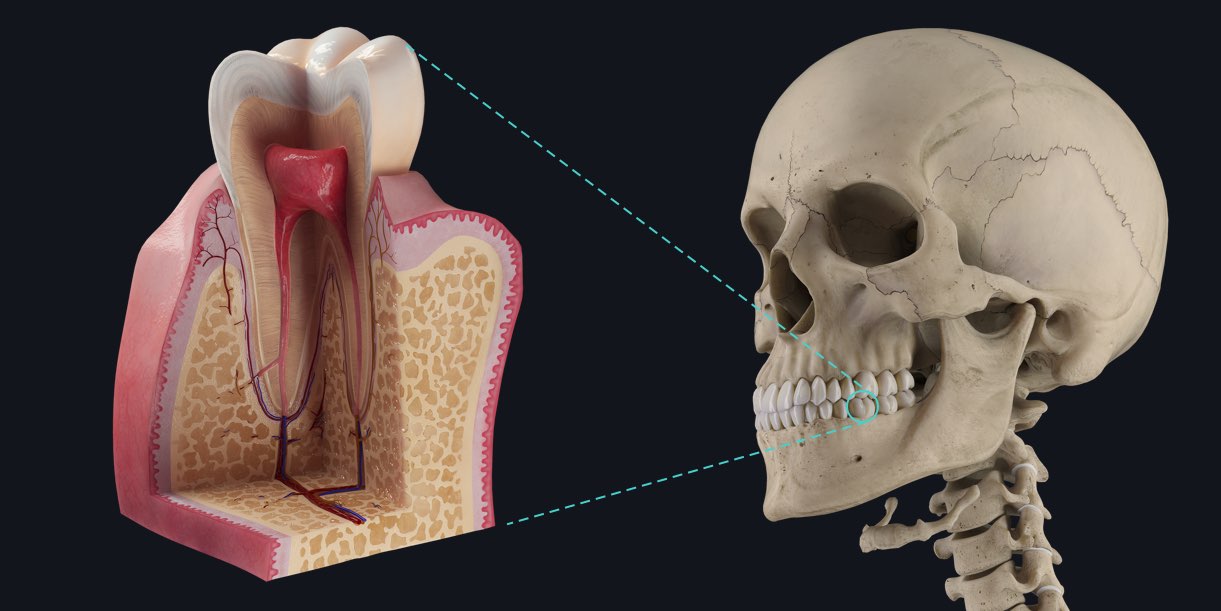
Although the arrangement of your teeth is as unique as your fingerprint, ultimately our teeth all have the same functions. Along with the lips and tongue, teeth help form words by controlling airflow out of the mouth. They also tear, cut and grind food in preparation for swallowing.
Cavities occur as a result of acid-caused tooth decay. It occurs when foods containing carbohydrates are deposited on the teeth, then the bacteria which reside in the mouth digest the food, resulting in the formation of acids. The bacteria, acid, food debris and saliva form plaque, which clings to the teeth, and the acid present in the plaque dissolves the enamel surface of the teeth, creating holes – cavities.
There are 4 major tissues associated with your teeth.
Tooth decay generally affects 2/4 of the tissues, the enamel and the dentin layer. In some cases it can also affect the pulp.
Enamel
Enamel is the outermost layer of the crown of the tooth and is responsible for protecting the underlying tooth dentine.
The composition of enamel is unique amongst mammal tissues, containing 96% inorganic material, 1% organic material and the rest water.
Dentine
The primary structural component of the tooth, it supports the enamel to maintain rigidity of the tooth and it protects the pulp cavity. Primary dentine is formed before eruption. Secondary dentine is produced after the root of the tooth is completely formed. Tertiary dentine, is created in response to a stimulus, and is often referred to as reparative dentin.
Cement
Cement is a hard, bone-like tissue covering the root surface of the tooth.
Throughout life, it is continuously produced through the process of cementogenesis, ensuring secure attachment of the tooth as the superficial layer of cement ages.
Dental pulp
This tissue resides in the chamber of the tooth, it is the living region of the tooth and is composed of connective tissue, blood vessels and nerves. It plays a major role in stimuli recognition and providing nutritive support to other areas of the tooth.
The tooth is one of many microanatomy models available with a Premium license from Complete Anatomy. To explore this, and 15 other detailed anatomy model, try Complete Anatomy for FREE today.