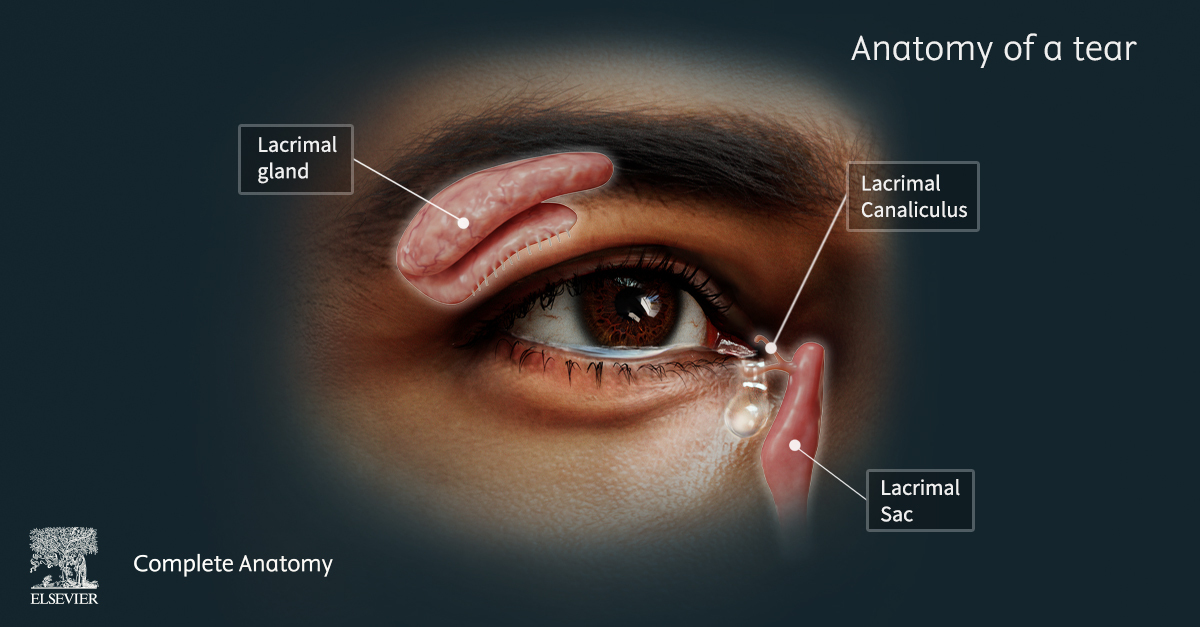
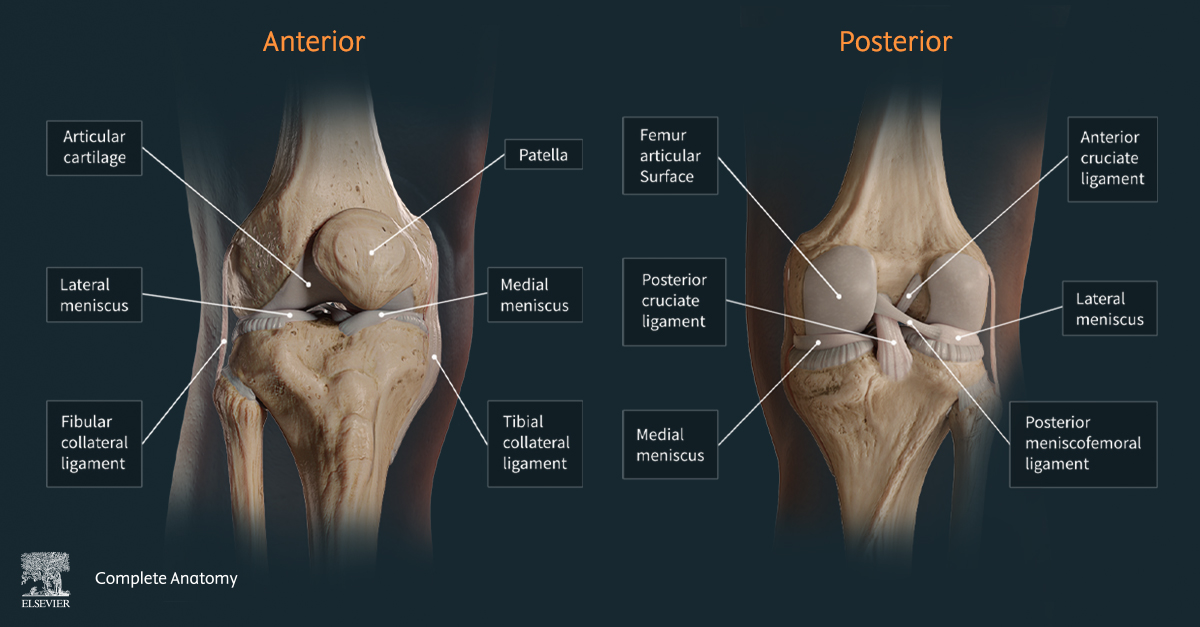
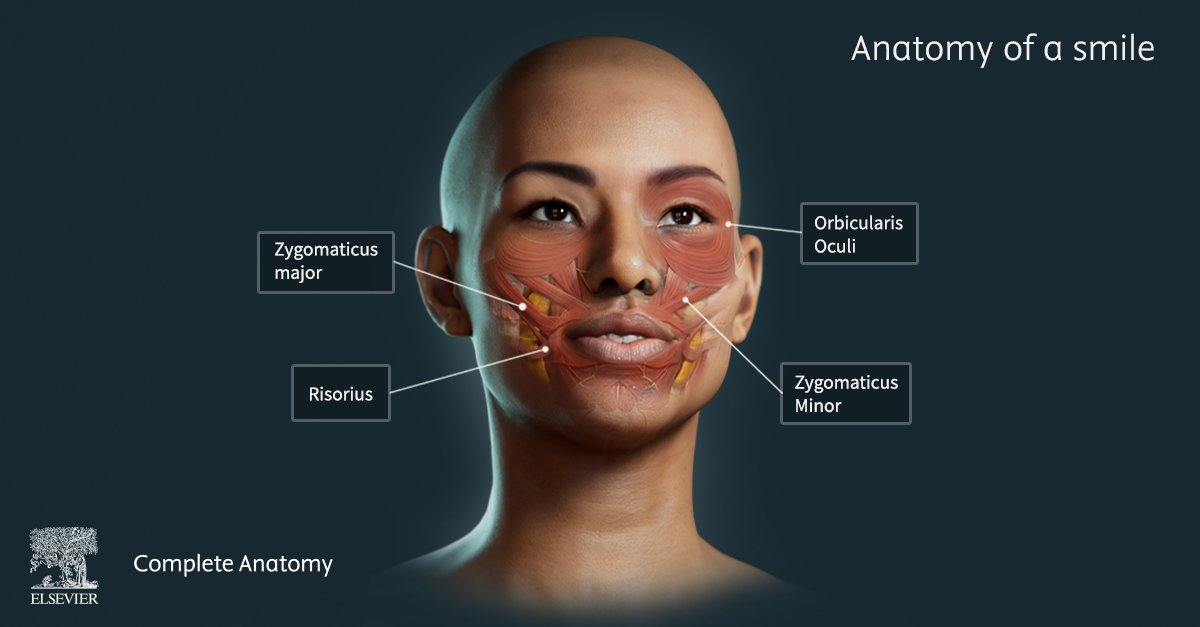
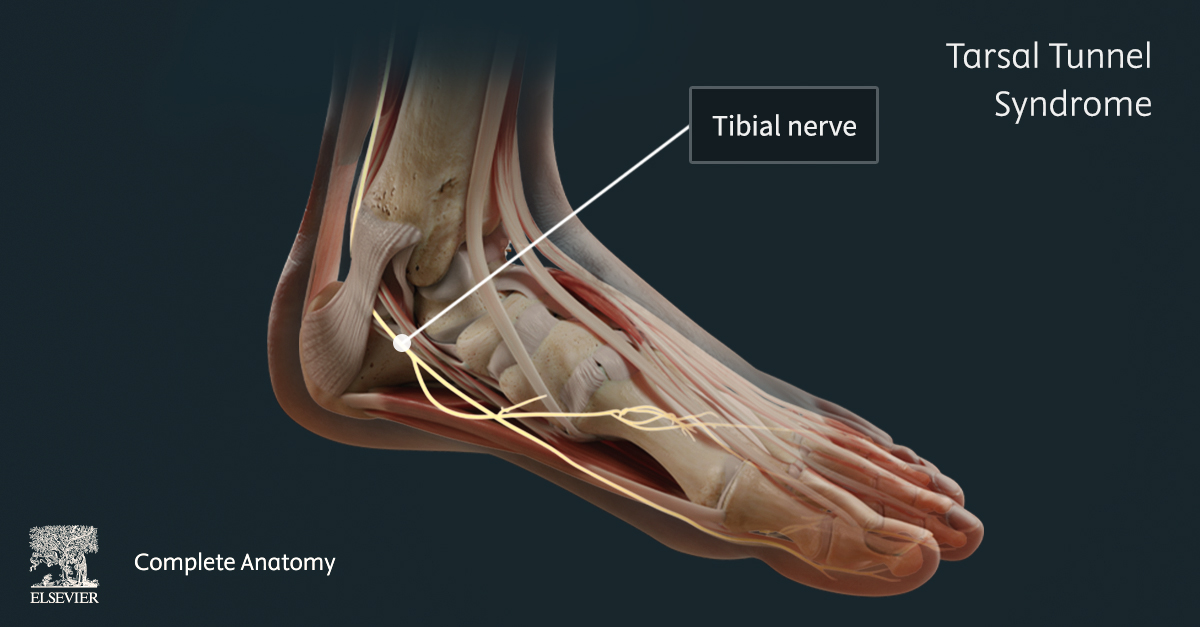
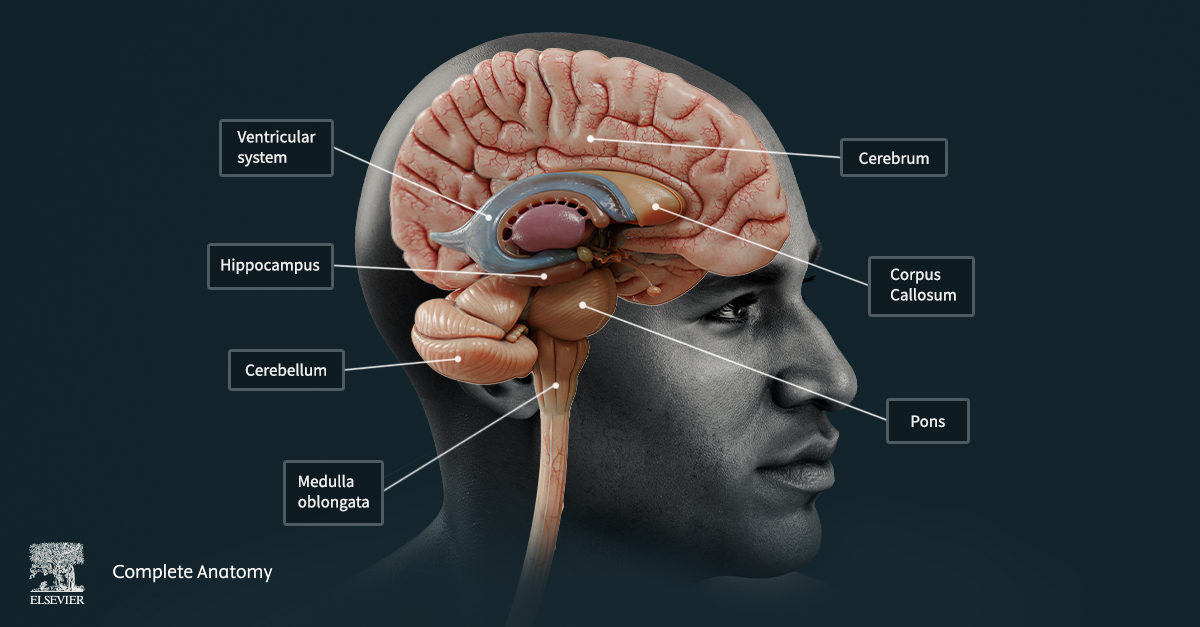
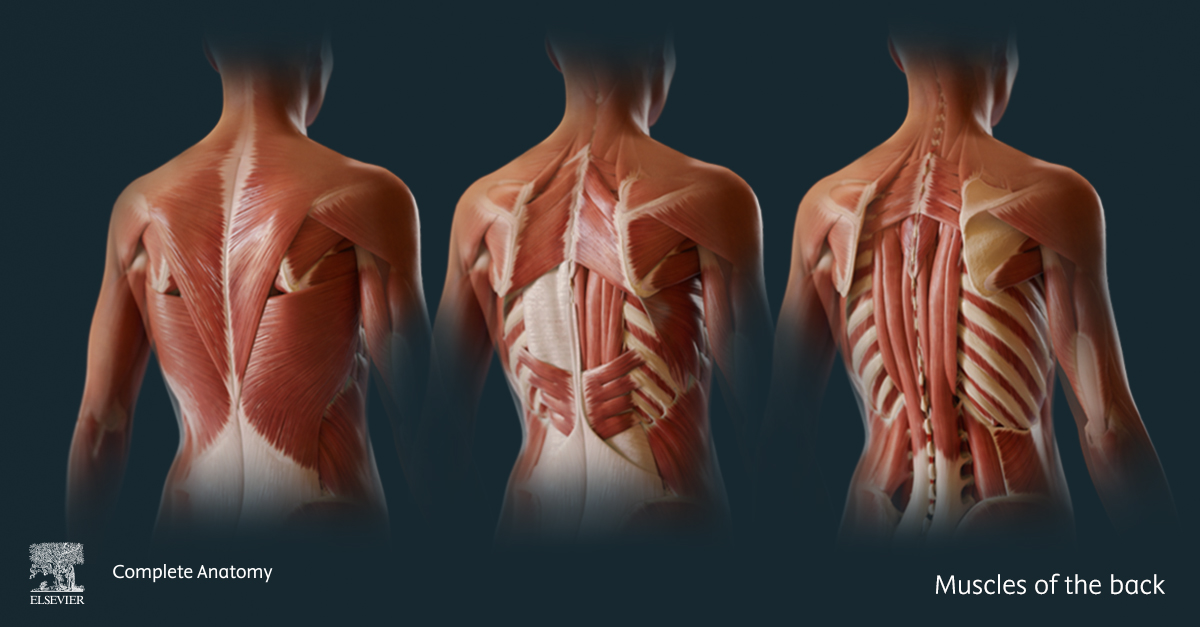
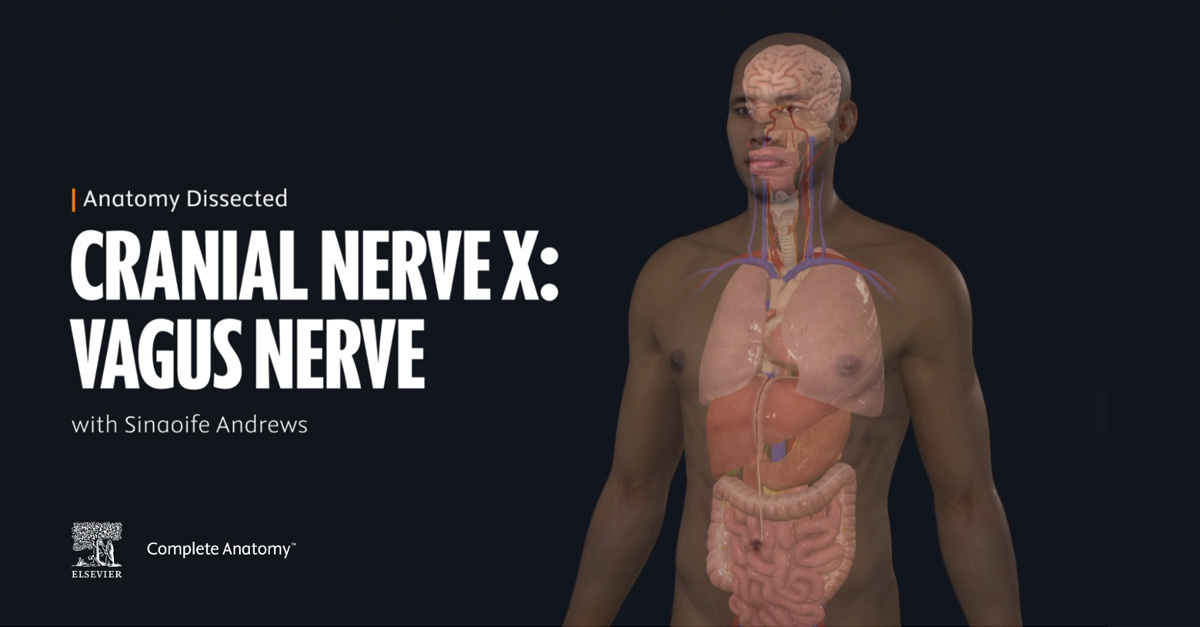
7 Ways Virtual Dissection Labs Can Benefit Your Program If you teach anatomy, you’ve seen how expectations around learning have shifted. Virtual dissection labs continue to emerge as a powerful complement or modern alternative to traditional cadaver labs. With advances in 3D visualization, interactive software, and remote access, these tools are becoming a go-to option for programs looking to adapt to changing educational […]Lire l’article